Is Cheating Illegal in 2026? An In-Depth Legal Analysis
The question of whether cheating is illegal in 2026 might seem straightforward, but the legal landscape is more nuanced than one might initially assume. While the term “cheating” commonly refers to acts of dishonesty in personal relationships, academic settings, or games, its legal implications vary significantly depending on the context. This article delves into the various forms of cheating, examines the existing legal frameworks, and projects how these might evolve by 2026. We will explore whether certain types of cheating could constitute criminal offenses or civil violations, considering the potential for new legislation and technological advancements to reshape the legal definitions and consequences of cheating. The goal is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the legal status of cheating as we approach 2026.
Defining Cheating: A Multifaceted Concept
Before examining the legality of cheating, it’s crucial to define what constitutes cheating. The term encompasses a wide range of behaviors, including:
- Infidelity in Relationships: Extramarital affairs or breaches of trust in romantic partnerships.
- Academic Dishonesty: Plagiarism, using unauthorized aids during exams, or collaborating on assignments when prohibited.
- Gambling Fraud: Manipulating games of chance, card counting, or using insider information for personal gain.
- Contractual Breaches: Violating the terms of an agreement through deceptive practices.
- Sporting Violations: Using performance-enhancing drugs or engaging in unsportsmanlike conduct to gain an unfair advantage.
Each of these scenarios carries different ethical and potential legal implications. While some forms of cheating may be morally reprehensible, they may not necessarily be illegal under current laws. However, certain actions can cross the line into illegal territory, especially when they involve fraud, theft, or the violation of specific statutes.
The Legality of Infidelity in 2026
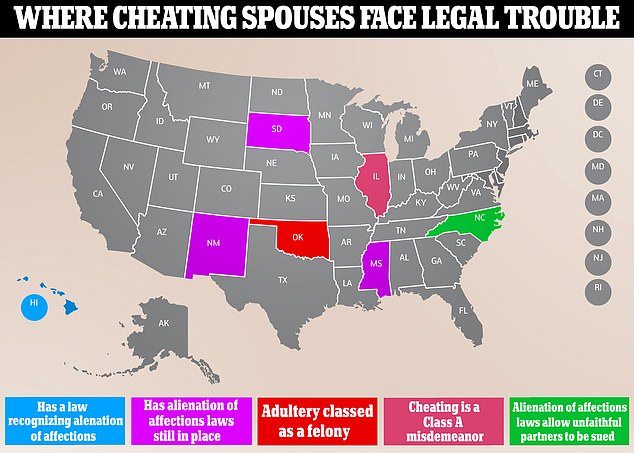
In most jurisdictions, infidelity, or extramarital affairs, is not a criminal offense. Historically, some regions had laws against adultery, but these have largely been repealed or are rarely enforced. However, infidelity can have legal consequences in the context of divorce proceedings. In some “fault” divorce states, adultery can be a factor in determining alimony, property division, and child custody arrangements. By 2026, the trend towards no-fault divorce is likely to continue, potentially diminishing the legal impact of infidelity. Nonetheless, the emotional and financial ramifications of infidelity can be significant, even if it doesn’t result in criminal charges.
Academic Dishonesty: Legal and Institutional Ramifications
Academic cheating, such as plagiarism or using unauthorized aids, is generally not a criminal offense. However, it can lead to severe consequences within educational institutions. Students caught cheating can face penalties ranging from failing grades to suspension or expulsion. These institutional sanctions are designed to uphold academic integrity and ensure fair evaluation of student performance. While not illegal in the traditional sense, academic cheating can have long-term effects on a student’s educational and professional prospects. Furthermore, if academic cheating involves copyright infringement (e.g., selling or distributing copyrighted course materials), it could potentially lead to legal action by the copyright holder. By 2026, with the increasing prevalence of online education, institutions may adopt more sophisticated methods for detecting and preventing academic dishonesty, potentially leading to stricter enforcement of academic integrity policies.
Gambling Fraud: A Clear Legal Violation
Cheating in gambling is almost universally illegal. Laws prohibit various forms of gambling fraud, including:
- Using Marked Cards or Loaded Dice: Manipulating gaming equipment to gain an unfair advantage.
- Collusion: Working with other players to deceive the casino or other participants.
- Insider Information: Using confidential information to place bets with a higher probability of winning.
- Online Gambling Fraud: Hacking into online gambling platforms or using bots to automate gameplay.
These activities are often classified as fraud or theft and can result in criminal charges, fines, and imprisonment. Gaming regulations are becoming increasingly stringent, with advanced surveillance technologies and sophisticated data analysis techniques used to detect and prevent cheating. By 2026, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in gambling security systems is likely to enhance the detection and prevention of fraudulent activities, making it even more difficult for cheaters to succeed without facing legal consequences. [See also: Online Gambling Regulations in 2025]
Contractual Breaches and Deceptive Practices
Cheating in the context of contractual agreements can lead to civil lawsuits for breach of contract. If one party intentionally misrepresents facts or conceals information to induce another party to enter into a contract, this can constitute fraud, which is a legal violation. Remedies for breach of contract can include monetary damages, specific performance (requiring the breaching party to fulfill their contractual obligations), and rescission of the contract (canceling the agreement). The legal principles governing contracts are well-established, and while specific laws may evolve over time, the fundamental principles are likely to remain consistent by 2026. Businesses and individuals should ensure they have clear and enforceable contracts to protect themselves from deceptive practices.
Sporting Violations: Rules, Regulations, and Legal Repercussions
Cheating in sports, such as using performance-enhancing drugs or engaging in unsportsmanlike conduct, is primarily governed by the rules and regulations of individual sports organizations. These organizations have the authority to impose sanctions on athletes who violate their rules, including suspensions, fines, and disqualifications. In some cases, sporting violations can also have legal consequences. For example, if an athlete provides false testimony in a doping investigation, they could face perjury charges. Additionally, the sale or distribution of illegal performance-enhancing drugs can result in criminal charges. As sports become increasingly professionalized and lucrative, the pressure to win can lead to more sophisticated forms of cheating. By 2026, sports organizations are likely to implement even stricter anti-cheating measures, including advanced drug testing protocols and enhanced surveillance technologies. [See also: The Future of Anti-Doping Technology]
The Role of Technology in Cheating and its Detection in 2026
Technology plays a dual role in the context of cheating. On one hand, it provides new avenues for engaging in dishonest behavior, such as online gambling fraud, academic plagiarism facilitated by AI, and the use of sophisticated devices to gain an unfair advantage in sports. On the other hand, technology also offers powerful tools for detecting and preventing cheating. AI-powered plagiarism detection software, advanced surveillance systems, and sophisticated data analysis techniques are increasingly used to identify fraudulent activities. By 2026, the interplay between technology and cheating is likely to become even more complex, requiring constant adaptation of legal frameworks and enforcement strategies to keep pace with technological advancements. The legal system will need to address emerging challenges related to digital cheating, such as the use of deepfakes to deceive others or the manipulation of online platforms to gain an unfair advantage. [See also: AI and the Future of Fraud Detection]
Potential Legal Developments by 2026
Looking ahead to 2026, several potential legal developments could impact the definition and consequences of cheating:
- Increased Regulation of Online Activities: As online activities become more pervasive, governments may introduce new laws to regulate online gambling, protect consumers from online fraud, and combat cybercrime.
- Stricter Enforcement of Intellectual Property Rights: Efforts to combat online piracy and plagiarism are likely to intensify, potentially leading to stricter penalties for copyright infringement.
- Enhanced Data Privacy Laws: Regulations governing the collection and use of personal data could impact the ability of organizations to monitor and detect cheating.
- New Laws Addressing Emerging Technologies: Governments may introduce new laws to address the ethical and legal challenges posed by emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and blockchain.
These potential developments highlight the dynamic nature of the legal landscape and the need for ongoing adaptation to address the evolving forms of cheating.
Conclusion: Navigating the Legal Landscape of Cheating in 2026
In conclusion, the question of whether cheating is illegal in 2026 depends on the specific context and the applicable laws. While some forms of cheating, such as infidelity, may not be criminal offenses, others, such as gambling fraud and contractual breaches involving deception, can have significant legal consequences. The increasing role of technology in both facilitating and detecting cheating adds another layer of complexity to the legal analysis. As we approach 2026, individuals and organizations should stay informed about the evolving legal landscape and take proactive measures to protect themselves from the risks associated with dishonest behavior. Understanding the legal ramifications of various forms of cheating is essential for navigating the complex ethical and legal challenges of the modern world. The future legal status of cheating will depend on how societies adapt to technological advancements and address emerging ethical dilemmas. Whether it’s preventing academic dishonesty, combating gambling fraud, or ensuring fair competition in sports, the legal system will play a crucial role in maintaining integrity and upholding the rule of law.
